Overview
This tutorial shows you how to make a Kubernetes deployment confidential using Contrast. We'll start with from a non-confidential deployment of a simple application.
Workflow
In this tutorial, we’ll use the emojivoto app as an example and walk through the steps needed to make a Kubernetes deployment confidential. You can either follow along or apply the same steps to your own application.
To make your app confidential with Contrast, follow these steps:
-
Install the Contrast CLI: Download and install the Contrast CLI, which is used to manage your deployments and generate necessary configurations.
-
Install and set up: Prepare your Kubernetes cluster to support confidential containers.
-
Deploy your workload: Update your application’s deployment to run with Contrast:
- Adjust deployment files: Modify your Kubernetes resources to integrate Contrast.
- Deploy the Contrast runtime: Run your workloads inside Confidential Virtual Machines (CVMs) by adding the Contrast runtime.
- Add the Contrast Coordinator: Include the Coordinator to verify and enforce the confidential and trusted state of your application.
- Generate policy annotations and manifest: Use the Contrast CLI to generate a manifest that defines the expected secure state of your deployment.
- Deploy your application: Apply the updated deployment files to launch your app.
- Set the manifest: Define the trusted reference state that the Coordinator will enforce.
-
Verify deployment: Confirm that your application is running securely and that workload integrity is being enforced.
-
Securely connect to the app: Establish a secure connection backed by confidential computing hardware—eliminating the need for users to place trust in you as the service provider.
Emojivoto app
We use the emojivoto app as example. It's a microservice application where users vote for their favorite emoji, and votes are shown on a leaderboard.
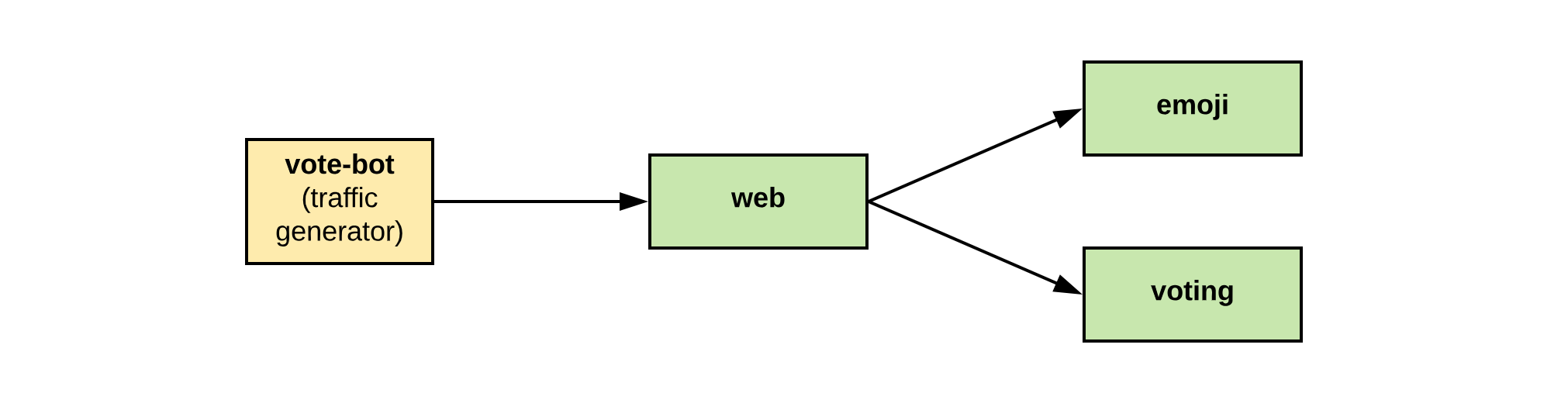
The app includes:
- A web frontend (
web) - A gRPC backend that lists emojis (
emoji) - A gRPC backend for handling votes and leaderboard logic (
voting) - A
vote-botthat simulates users by sending votes to the frontend
Emojivoto is a fun example, but it still handles data that could be considered sensitive.
Contrast protects emojivoto in two key ways:
- It shields the entire app from the underlying infrastructure.
- It can be configured to block data access even from the app's administrator.
In this setup, users can be sure that their votes stay private.